Top 11 Software Development Trends 2024 – 2025 (Part 2)

Top 11 Software Development Trends 2024 – 2025 (Part 2)
Where will software and tech take us soon? Let’s go further on and find out.
6. Continued expansion of the IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is set to continue expanding in 2024 and beyond. Statistics show that there will be 65 billion IoT devices in 2025. That’s 6x more than in 2018.
In late 2020, the number of IoT connections surpassed non-IoT connections. In particular, smart speakers are expected to continue in an upward trend. Data shows the market could be worth $35.5 billion in 2025.
Forrester predicts that wearables and sensors aimed at allowing patients to monitor their health at home will surge in 2021 and beyond. The data collected from the patients can enable doctors to be proactive in medical treatments and improve care.
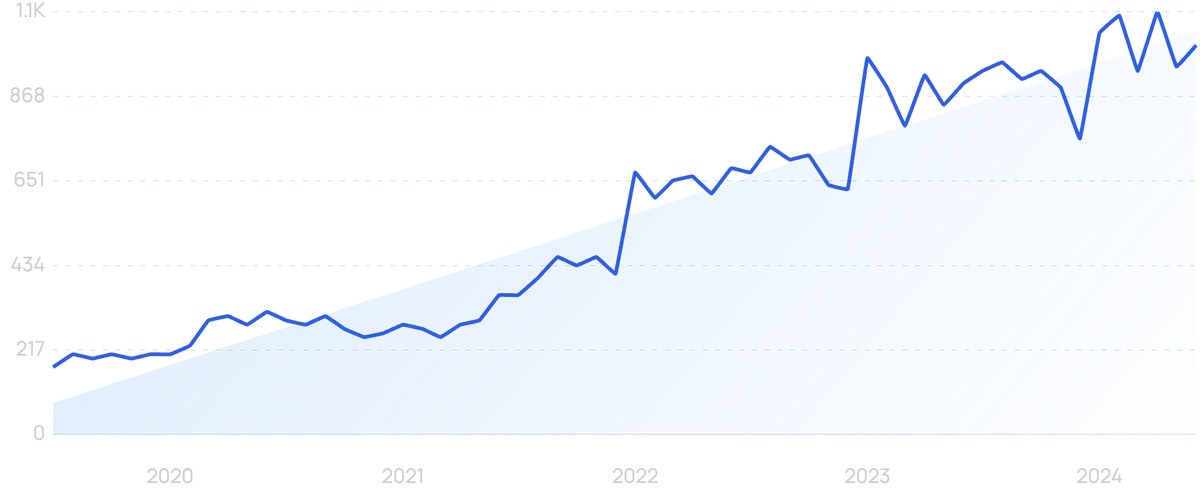
Searches for “remote healthcare” have increased by 475% over the past 5 years and have remained high since the pandemic.
The IoT goes way beyond use in homes. Bayer recently developed an inexpensive IoT chip that’s similar to a mailing label.
It can be attached to anything from chemical compounds to seed packs to track items after leaving the warehouse and throughout distribution.
7. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) Aim to Provide a Better User Experience
Smartphone users want their app experience to be fast and reliable, but often, they don’t want to download apps because they take up too much space. Google found that half of smartphone users are likely to use a brand’s mobile site because they don’t want to download an app.
Many companies are turning to progressive web apps (PWAs) to find a solution. These offer the ideal combination of standard website technology and the convenience of an app.
Developers tout PWAs as the best of both worlds.
PWAs run on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript like websites do, but they take away the browser interface and borders. Unlike native apps, users do not need to download PWAs. They simply save them to their home screens.
PWAs load quickly and send push notifications just like a native app. And, because they cache data, they’re even available offline.
One attribute that makes PWAs increasingly popular with developers is that they’re platform agnostic — developers don’t have to build a separate app for mobile, tablet, and desktop.
One estimate says PWAs can cost up to 15 times less than a normal mobile app.
Starbucks is one company that’s already taking full advantage of the benefits of a PWA. And it’s 99.84% smaller than the brand’s iOS mobile app.
Since implementing the PWA, Starbucks has doubled the number of web users who place orders each day.
8. Microservices Architecture Simplifies Deployment and Scaling
Technavio reports that the growth of the cloud microservices market is accelerating. They predict the CAGR will surpass 25% through 2026, adding $1.59 billion in market value.
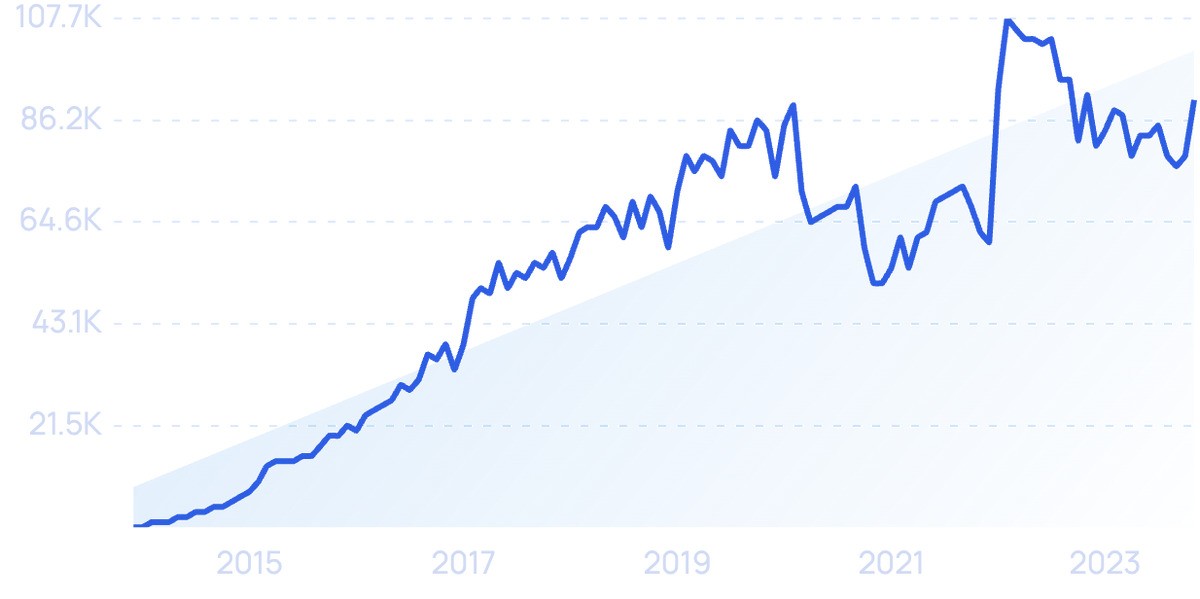
Search volume for “microservices” is up 2,400% in the past 10 years.
Microservices architecture represents a new approach to software development.
The old approach, monolithic architecture, involves all the application processes being coupled together and run as a single service.
Because all of the code is grouped together, changing one process means changing the entire application. This approach is neither agile nor scalable.
On the other hand, microservices architecture features modules built as independent services. Each of these modules supports a specific task or goal and uses an API to communicate with other sets of services.
The modules can be built, managed, and changed without altering other modules.
This new structure means microservices require less development time and can be scaled easily. They can also be reused in other projects. IT teams also save time and money when a problem occurs.
If something goes wrong in a monolithic architecture, teams have to troubleshoot, test, and update the entire software. With microservices, the fault is isolated, remediated, and redeployed within a single service.
In a 2021 IBM survey, 88% of current microservices users said they agree or agree completely that microservices architecture offers many benefits to their development teams and 87% agree or completely agree that the effort and expense of adopting this approach will be worth it.
One of the most popular tools to use within microservices architecture is Docker.
Docker provides containers that encapsulate each service. Each container has the source code and operating system libraries required to run that service in any environment.
This becomes incredibly useful in automating the deployment of applications.
9. Use of Blockchain in Software Development Expands
The majority of the buzz surrounding blockchain technology has been focused on cryptocurrency. However, the technology has implications for the software development industry as well.
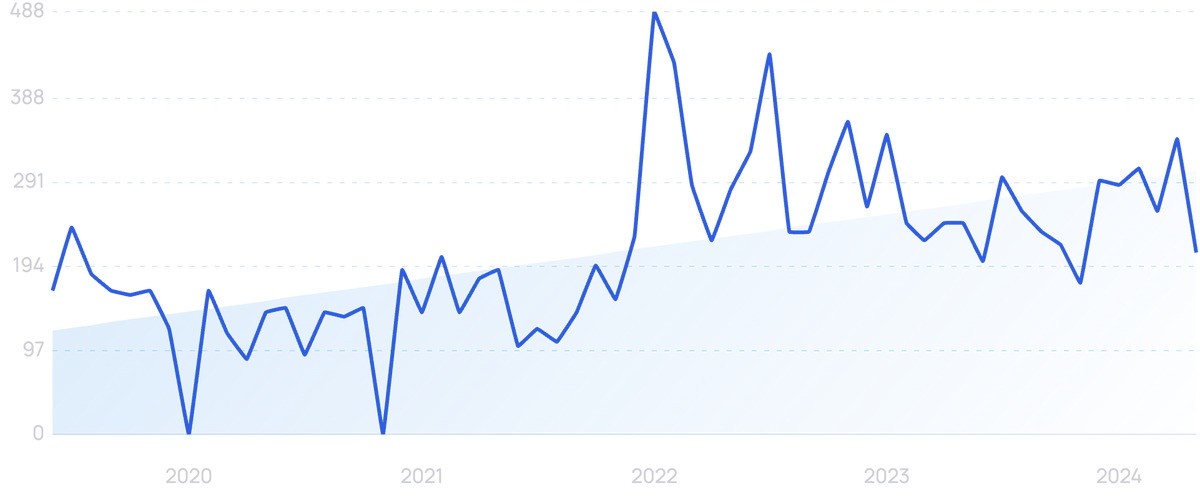
Search volume for “blockchain software development” is up 26% in the past 5 years.
Overall, the blockchain market is expected to grow to $291 billion by 2030 Businesses across the globe are implementing blockchain in their organizations.
A survey by Deloitte found that 73% of executives feel that blockchain can give them a competitive advantage.
There’s a good reason for this.
Blockchain-oriented software (BOS) systems are robust and incredibly secure. The data in the systems is replicated and decentralized, ensuring data security.
There’s also transaction recording and public-key cryptography, which add another layer of safety to the data. There’s little risk of hacking or theft because users can view and record the software but they cannot modify or delete any data.
One area in which the security of blockchain technology is particularly appealing is software development for the healthcare industry.
For example, blockchain-based systems can bring together pharmaceutical companies, hospitals, insurers, medical device OEMs, and others. They can log contract details, track transactions, and provide payment details.
They can also automate the terms of their contracts using a technology called smart contracts.
Another instance of blockchain-based software is a specific type of app called a decentralized application (dApp).
As its name implies, there’s no centralized place where the code is stored and it’s not owned by any specific company.
In practical terms, this means that the “middle man” is unnecessary. For example, users don’t need a company like Airbnb or Uber. Instead, they can directly access the platform and its services.
10. Companies Turn to Outsourcing in the Face of IT Skills Shortage
Executives are eager to implement emerging technologies, but they’re having to do so with fewer staff members than ever before. In the past, software developers were expected to have an academic background and training.
But, in today’s hiring climate, nearly 80% of HR professionals are open to hiring individuals who have been self-taught or trained in a bootcamp-style course.
IBM is one company that’s taking concrete steps to train the workforce it so desperately needs. The company announced an ambitious goal in October 2021: to train 30 million people by 2030.
Outsourcing is another way IT departments are looking to scale and stay agile while avoiding the headache of recruiting and the pinch of attracting new employees with high salaries.
The IT outsourcing market reached $522 billion in 2021 and is expected to swell to $689 billion by 2027.
In one example, CSX transitioned 137 in-house IT jobs to Mumbai-based TCS (Tata Consultancy Services) in July 2022.
In a similar move, OhioHealth eliminated 567 IT jobs, citing plans to outsource the positions to Accenture, a professional services company.
A representative from OhioHealth said, “We’ve realized the best way to deliver in IT is to leverage the tools, technology, and global talent pool external partners can provide. These are areas that continuously have rapid growth. By leveraging the deep expertise of our partners, we will keep pace with these rapid changes in a better way than we could on our own.”
11. DevSecOps Approach Integrates Security into the Development Process
The combination of development, security, and operations (DevSecOps) represents a new software development approach that integrates security throughout the entire IT lifecycle.
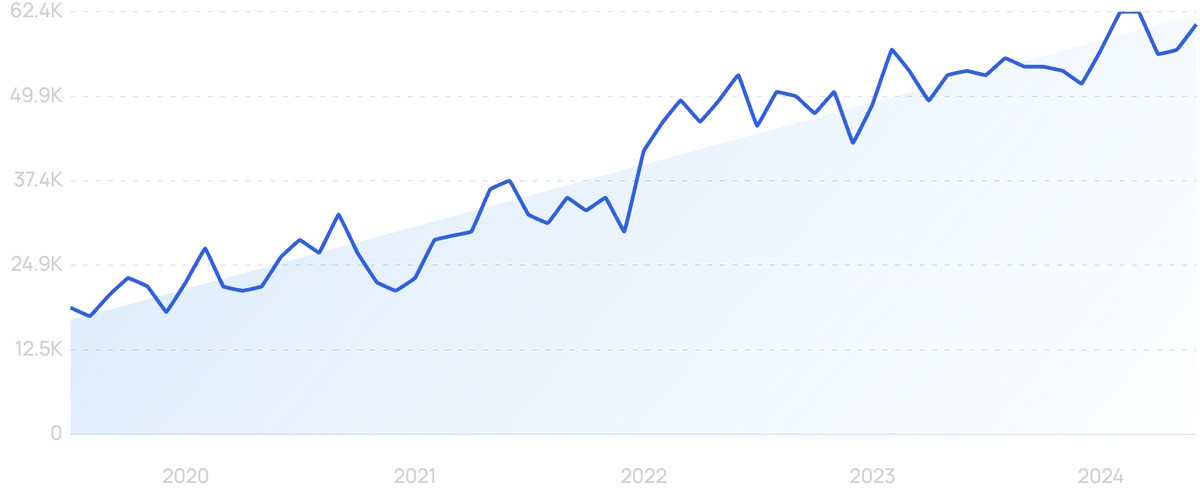
Search volume shows growing interest (200% in 5 years) in “DevSecOps”.
In the traditional development approach, there was plenty of time for the code to go through testing and security processes because new software was released every few months or even years.
Today, new features and code are being pushed out very quickly, so quickly that security testing cannot keep up.
The DevSecOps integration is crucial when it comes to implementing security without slowing down development or delaying releases. Instead of security being a concern at the tail end of the development process, developers can fix security issues in the code in real-time. The result is software that’s deployed as quickly as possible while being as secure as possible.
Many teams are adopting this approach. In a 2021 GitLab survey, 70% of security professionals said their teams had moved security earlier in the development process. That was compared to 65% in 2020.
However, there’s still internal debate regarding the DevSecOps strategy. The GitLab survey reported that 45% of security team members say that developers catch less than one-quarter of bugs in the code.
However, the ROI of utilizing the DevSecOps strategy is solid. Those organizations that use the strategy deploy code 46x more frequently than low-performing teams. These organizations also reduce costs 56% more effectively and are 144% more likely to resolve security flaws quickly.
Conclusion
That wraps up the 11 emerging trends in software development happening right now. Interconnectivity, automation, and cloud computing are likely to continue on the path of rapid adoption. However, these developments do come with challenges.
Are we, as a society, ready to integrate this much technology into our everyday lives? Hackers are betting on it and are ready to pounce on any vulnerabilities.



